Introduction
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
- Class: Security Governance
- Topic: Introduction
2. General Information
Google Classroom code: ebpgz6k see “Lavori del corso” for all the information about the exams, results and slides. Office Via Ariosto, 25 B114. All the readings necessary for the exam are published on google Classroom.
3. Introduction to Security Governance
We’ll study how to manage and structure policies, processes and reasons to consider when constructing a security infrastructure. We’ll not only consider a technical point of view, but we’ll take into account the vulnerabilities introduced by humans. So to really protect a system processes, humans and technical aspects have to be taken into account at the same time.
3.1. Enterprise
Every company has a mission, or an objective, like providing services, the final scope for which the company exists is the global objective. In order to develop it’s objective the company has to interact with people. People will interact with ICT infrastructure. The way in which the people interact with the ICT is crucial from the Security point of view. Policies are used to indicate how people have to interact with the ICT.
Very important is also the Company Organization, that is a gerarchical organization of roles and resposabilities of people inside the company; these roles and responsabilities plays an important role security wise.
3.2. Concept of Governance
The definition of Mark Bevir says that governance is the development of decisional processes taking into account the social organization with contraints on regulations, laws and norms.
The definition of Marc Hufy says that governance means taking decision among actors involved in a collective problem.
Governance deals with processes, which takes into accounts norms, or market regulations / best practices. There exesists different types of governance. Decisions could hapen at different levels.
- Enterprise Governance: control and direct the performance of an enterprise. Set of policies in order to monitor and take decision in order to improve the performances of a company.
- Business Governance: is the subset of enterprise governance strictly related to the business, so it is the set of decision used to improve the throughtput of production, leading to best revenue.
- Corporate Governance: it is the subset of processes aimed to direct and control the company. Controlling the quality of the production, or verifying the compliance of the business processes.
Security governange is a subset of the corporate governance.
3.2.1. Corporate Governance.
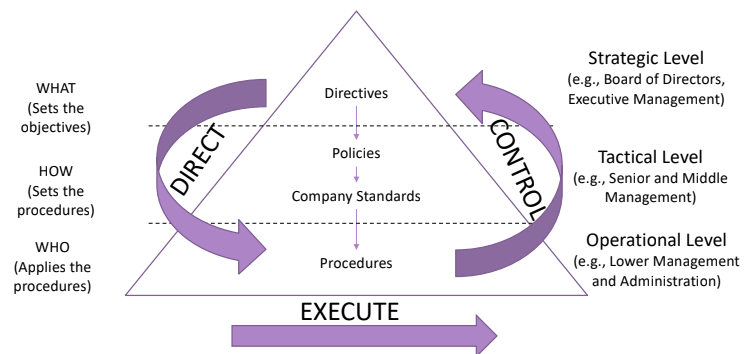
In order to control the compliance, We’ll use the direction piramid and observe how the decisions are taken through the different layers.
- Strategic Level: high managment, output the direction via directives.
- Tactical Level: defines the policies, and design internal standards outputting Company Standards. Policies are inspired by external standards that drive internal standards.
- Operational Level: where the procedures are concretely implemented.
Going from Strategic Level to Operational Level we talk about direct process, executing the processes. To monitor the goodnes of the processes we perform a control operation giving a feedback to check if the directives are enough or not. The objective is to continuosly improve the goodness of the governance. Direct Control Loop.
3.3. Context Overview
When considering security governance, the Direct Control Loop has to take into account threats and vulnerabilities that can be of different types. Technical like bugs, errors, or backgrounds; but also human like people that do not comply whith the policies; or the processes could be wrong, like having the best IDS without using it well.
The aim of the Direct Control Loop is to verify if the objectives are acheived by using measurements taken from the environment. To implement the direct control loop in Security Governance We have to use the foundamental concept of risk.
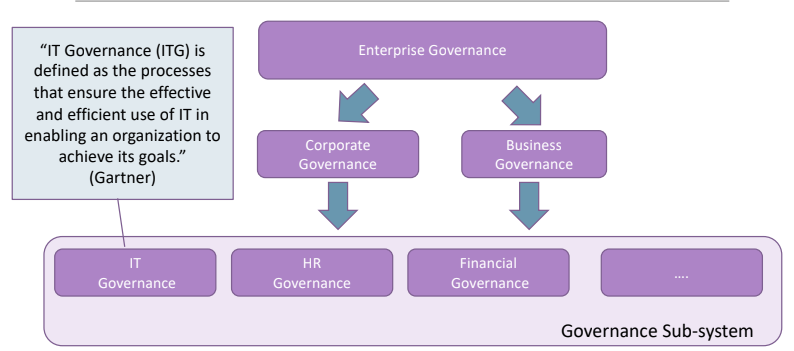
We’ll look to the IT subset of Corporate Governance.
3.4. IT Governance and Risks
Today every company uses some kind of IT infrastructure, exposing the company to certain types of risks. From the point of view of the Security Governance we want to preserve the CIA properties of data and information when they are stored, travelling and under processing.
In a complex environment an attacker can be inside or outside of the company and can use vulnerabilities to cause damages.
Security governance is the means by which you control and direct your organisation’s approach to security. — UK National Cynersecurity Centre
There’s no gold standard approach to security governance, there are plenty of approaches that varies to formal security frameworks to informal security frameworks. The correct answer depends on the environmnet, the regulatory contraints, and the stakeholders.
To identify in which portion of the spectrum we are we can answer some questions:
- How large and complex is your organisation?
- What resources are available for security governance? (Cost / Benefit tradeoff, a more formal approach is expensive)
- What is your business and how much the security is important to your business?
- Is there any contraints coming from external stakeholders? (Like building software for critical infrastructure, the environment can introduce additional contraints)
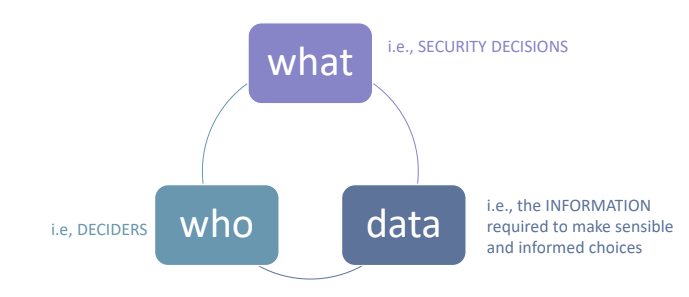
Answering this question will give a good starting point, then it is important to evaluate cost / benefit tradeoffs. Practically speaking we what to identify:
- What, security decisions
- Who, who selects the decisions
- Data
And how these three are linked togheter.
3.5. Why We should care about Security Governance?
Because we have an increasing role of Social Engineering in attacks against companies; from the verizon report we can see that 85% of breaches involved a human element; for this reason the policies have to take into account how peopleinteract with the ICT system, and managing credentials. Also it is important to take into account the fact that there is an increasing trend in attacks coming from organized crime outside the company.
Most of the time, the motivation behind a cyber attack is financial. Also during the last years the methodologies used by the attackers changed, We saw an increase of phising and ransomware attacks. he fact that the direct / control Loop has to be performed continuosly is justified by the fact that everiday new vulnerabilities are discovered. Data about people is the most valuable kind of data.
The distribution of causes of data breaches is for one fourth of the cases is beacuse of human errors.
3.6. Advanced Persistent Threat
3.7. Security Governance and Legislation
There are already existing laws that are relevant for information security, that impact the policies.
4. What we’ll learn
- One model for the information Security Governance
- Study main Cyber Security best practices, guidelines, and frameworks, and how to use them.
- How to assess and manage risks.
- Understanding threats, vulnerabilities and attacks
- Evaluate the impact
- Finding proper contermeasures
- How to modle and understand threats
- Legislation compliance and insurance
- Main research issues in the field (NLP is a related concept and a target for the future).